This post demonstrates the incremental load in SSIS with example. Based on the business requirement and data volume we should determine the ETL process. We’ll assume we have a low to mid-sized source data file and here are the requirements:
Tech Tip : Carry out complex database operations and monitor them remotely by migrating your Sql server into the cloud and access it remotely on your preferred device(PC/Mac/android/iOS) with cloud hosted virtual desktop from:
CloudDesktopOnline with dedicated migration support from www.Apps4Rent.com
ETL Requirement:
We have a distributed database system and getting customer information on daily basis to load into SQL Server instance by following the below conditions:
- Customer information is sending in flat file format
- We are getting Delta Data Feed that means it includes new, updated and deleted customer’s data.
- Compare Source (Flat File) and Destination (SQL Server) customer ID
- If no match found at destination: Insert Row into Destination
- If match found and IsDeleted = 1 / True: Delete the row from Destination
- If match found: Update row from source to destination
Note:
- We are using Sales.Customer from [AdventureWorks].
- Be cautious in using OLEDB Command for large datasets as it’s a row by row process and impact the performance.
- In case of doing incremental load for large datasets, load data into staging table and then update / delete using a query through Execute SQL Task.
ETL Solution Design:
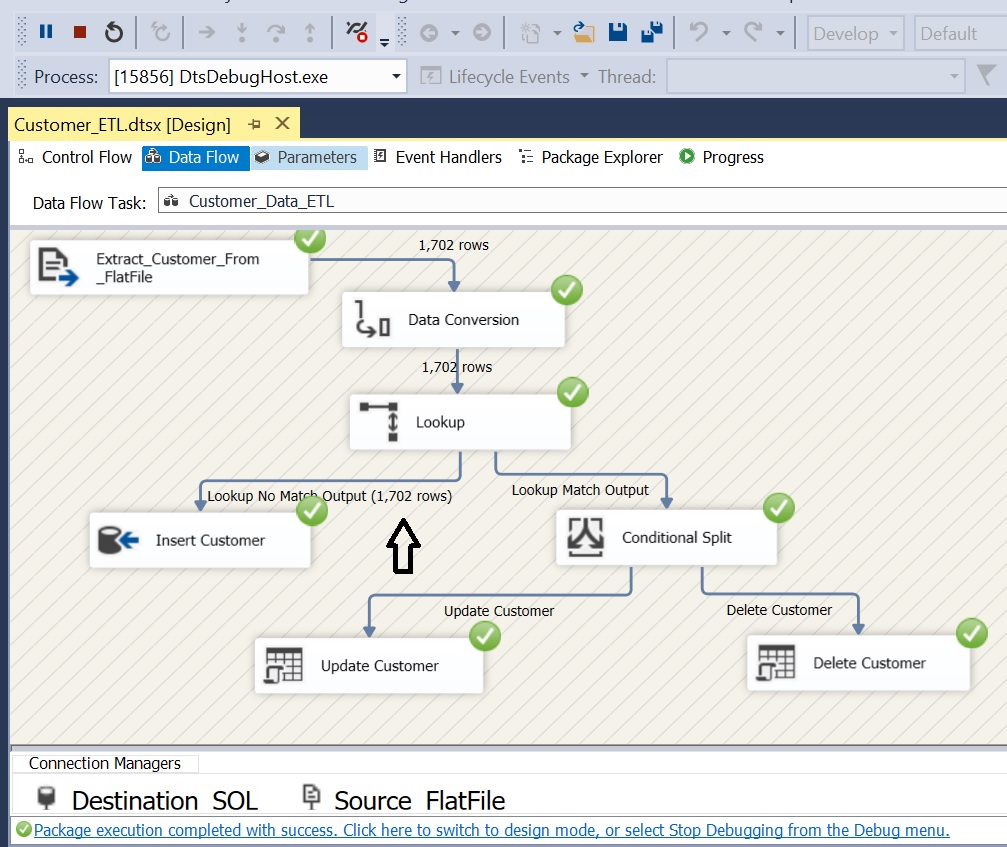
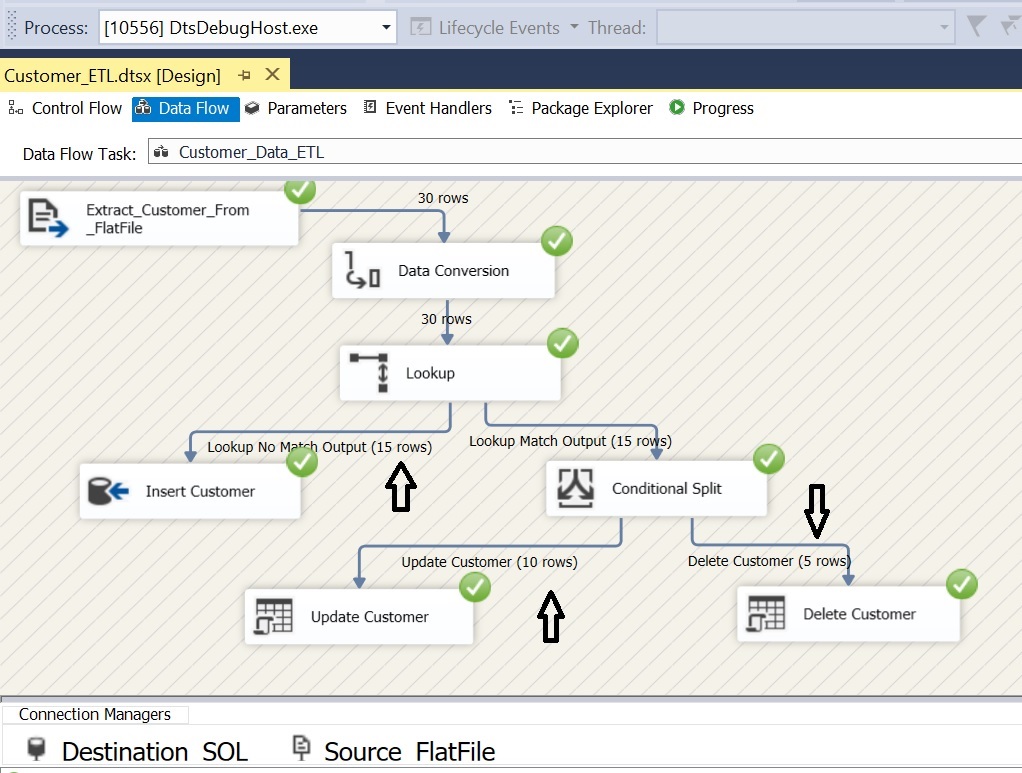
Flat File Source: To extract data from source flat file
Data Conversation: Convert source columns datatype to match the destination customer table
Lookup: Compare source and destination customerID column
- No-Match Output: When there is no match found in destination
- Match Output: When match found between source and destination
Conditional Split: Check if IsDeleted = 1 then redirect it to DELETE output. Redirect default output to UPDATE output.
OLEDB Destination: For inserting new records
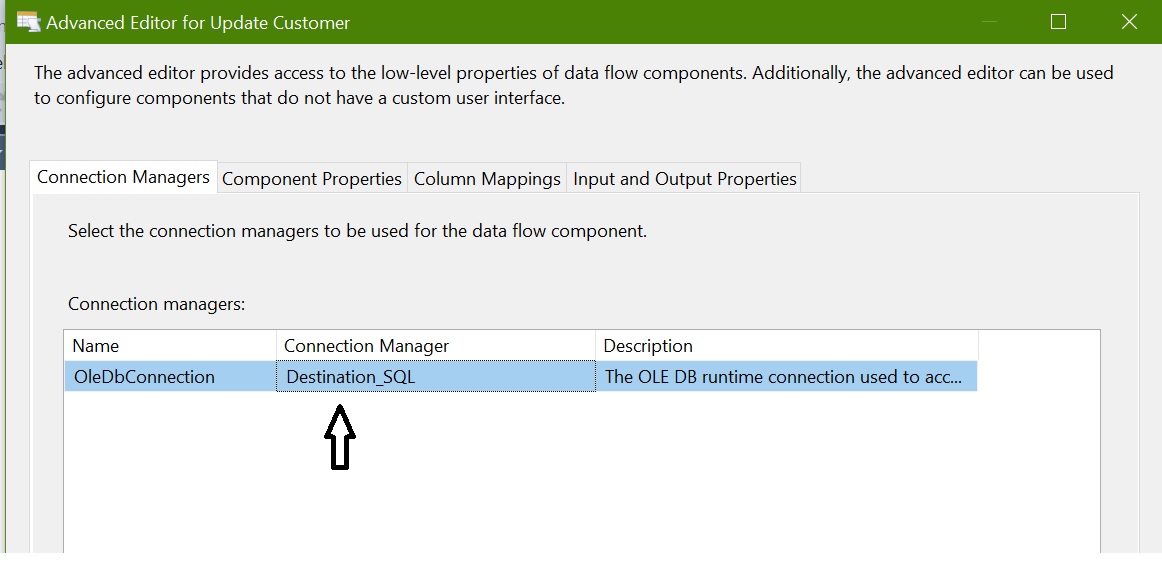
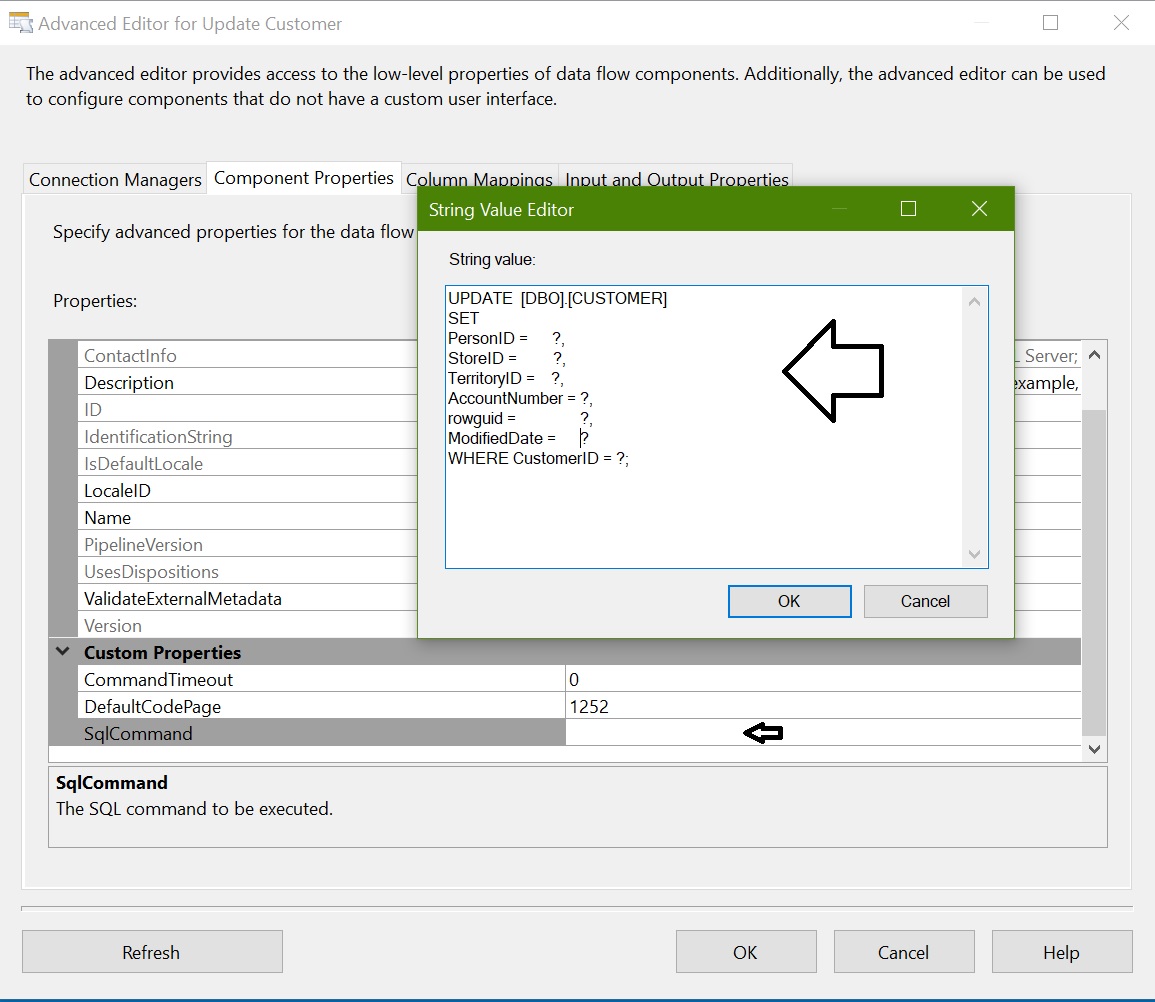
OLEDB Command (Update): For updating rows
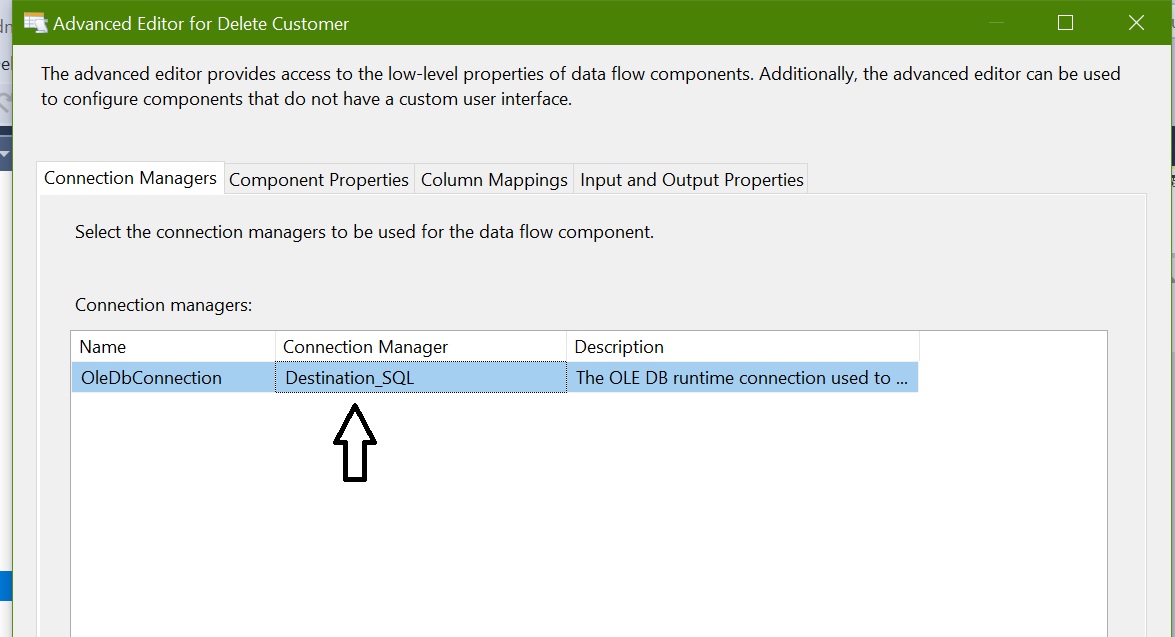
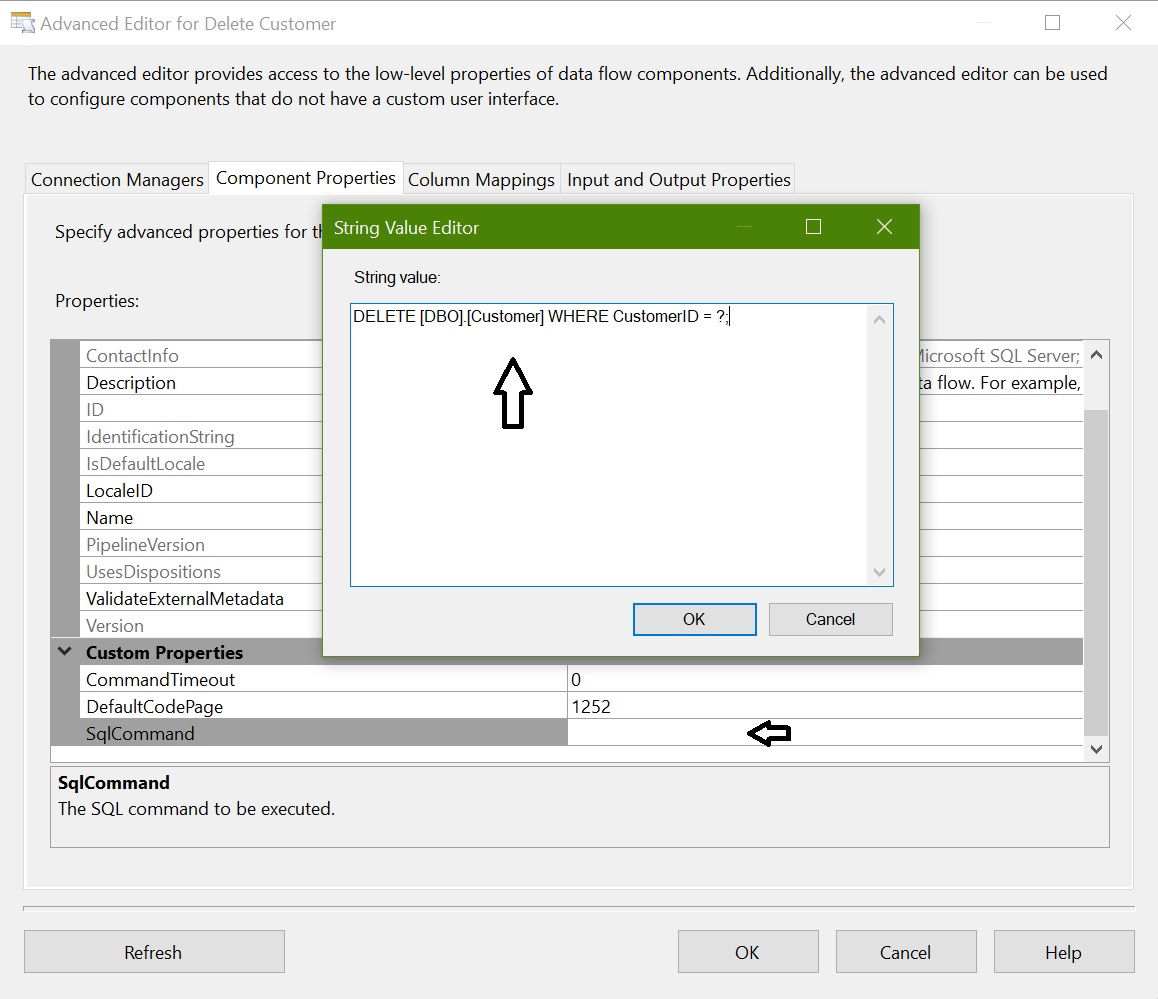
OLEDB Command (Delete): For deleting rows
ETL Package Design:
Open SQL Server Data Tools
Create a new Project name it as “Sales_ETL” and Package name it as “Customer_ETL”
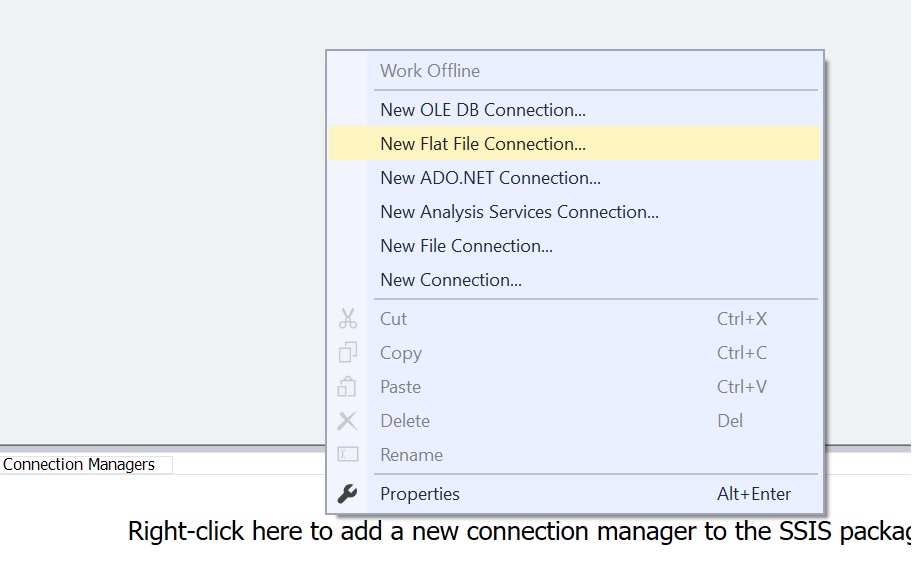
Create two connection managers 1) Source – New Flat File Connection 2) New OLE DB Connection
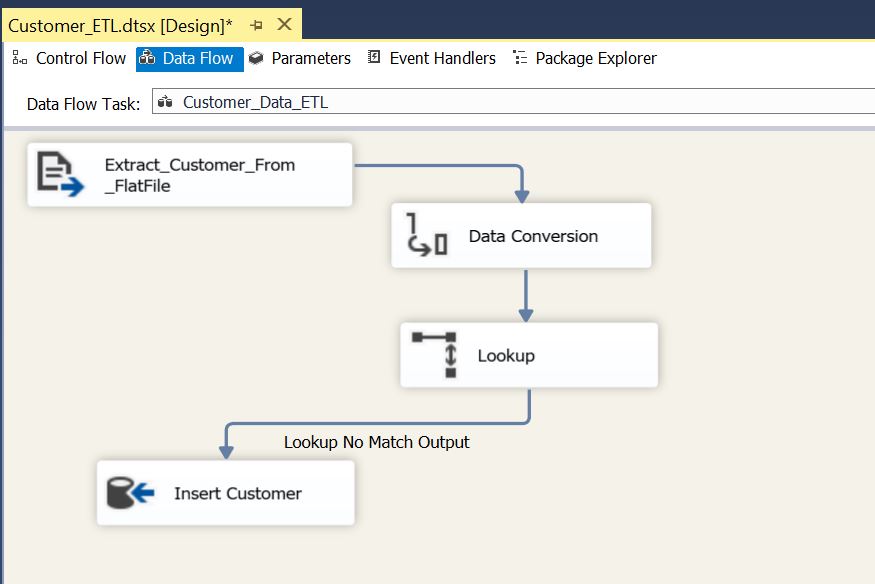
Add a Data Flow Task to Control Flow and name it as “Customer_Data_ETL”
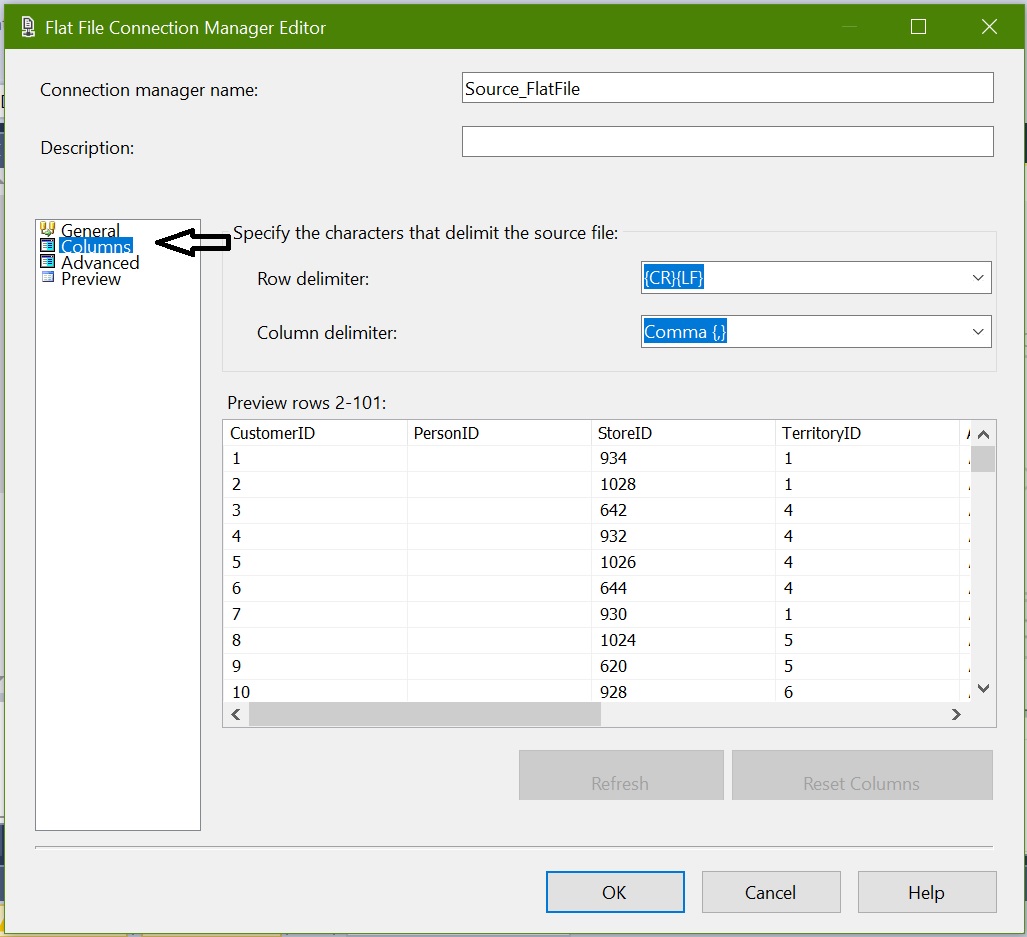
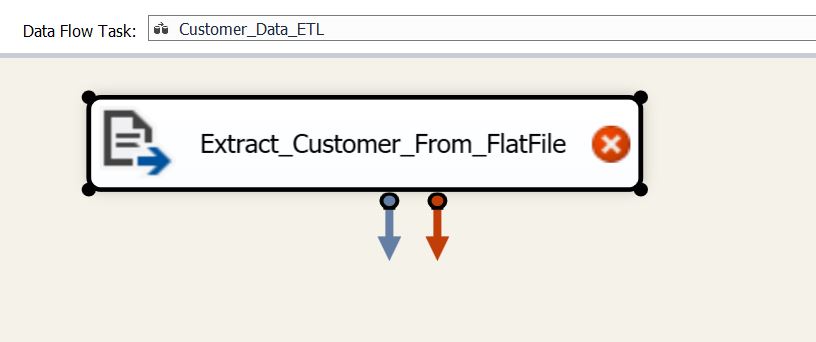
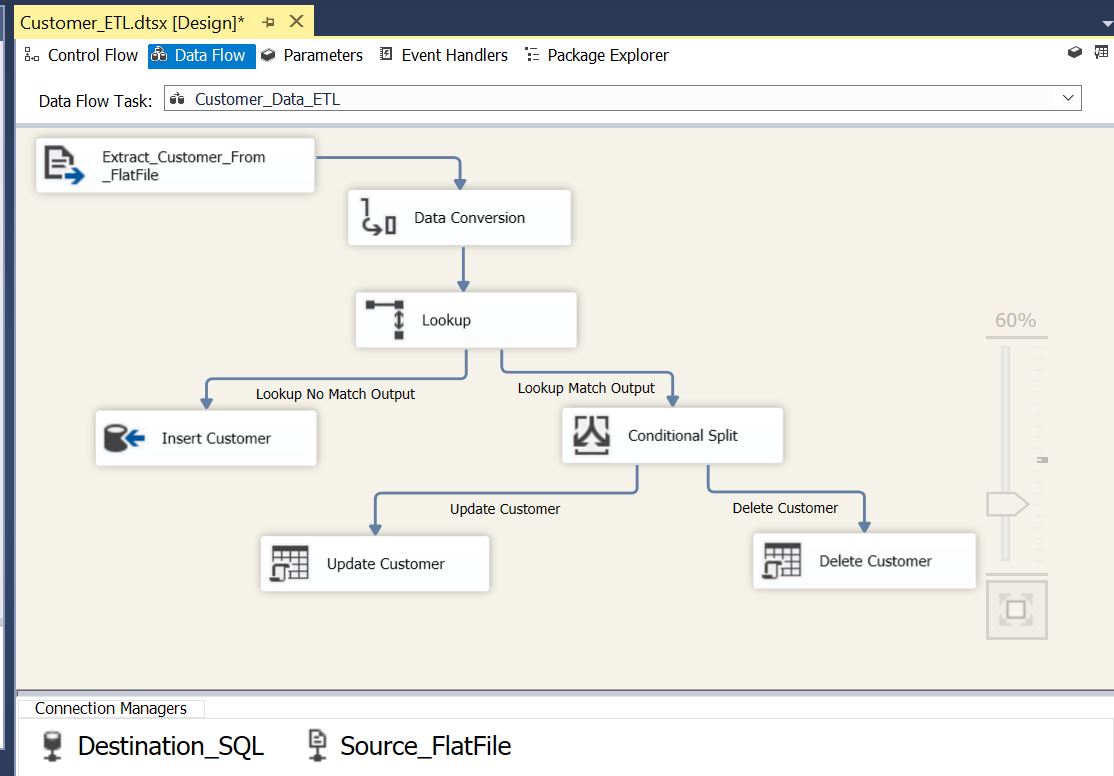
In Data Flow Task, add Flat File Source and name it as “Extract_Customer_From_FlatFile” and connect to the flat file source:
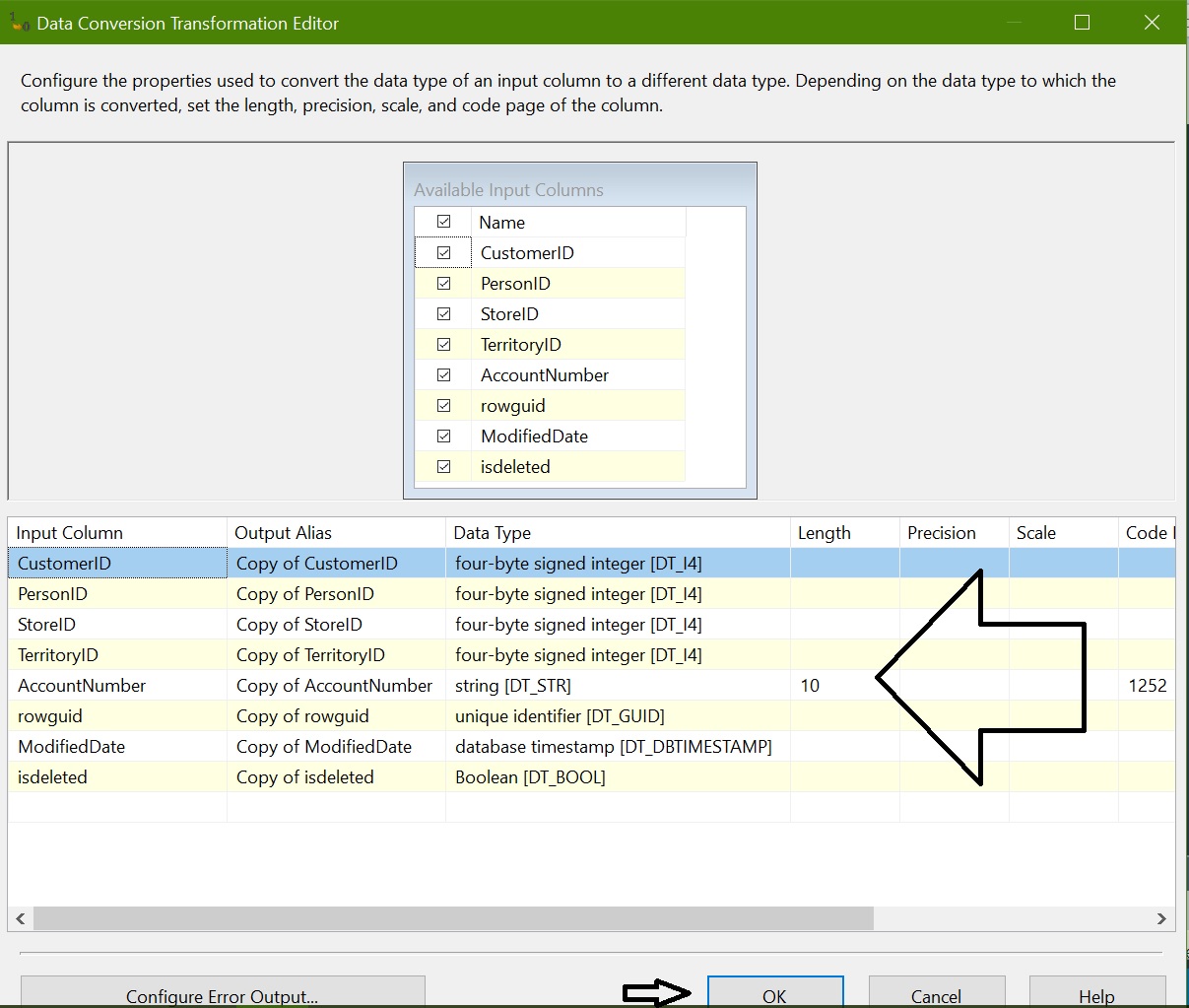
Add “Data Conversion” and convert datatype for all columns as per the destination table:
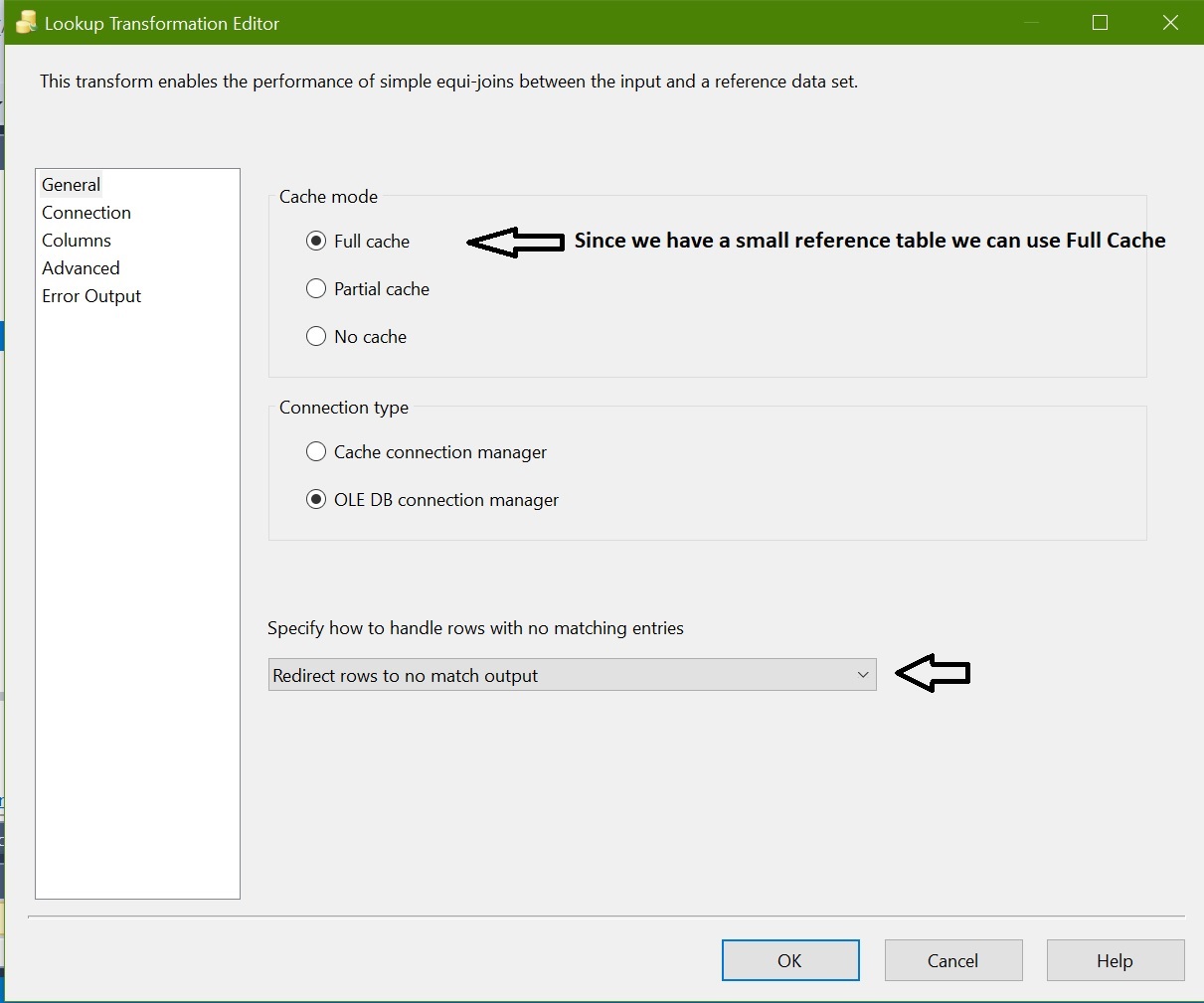
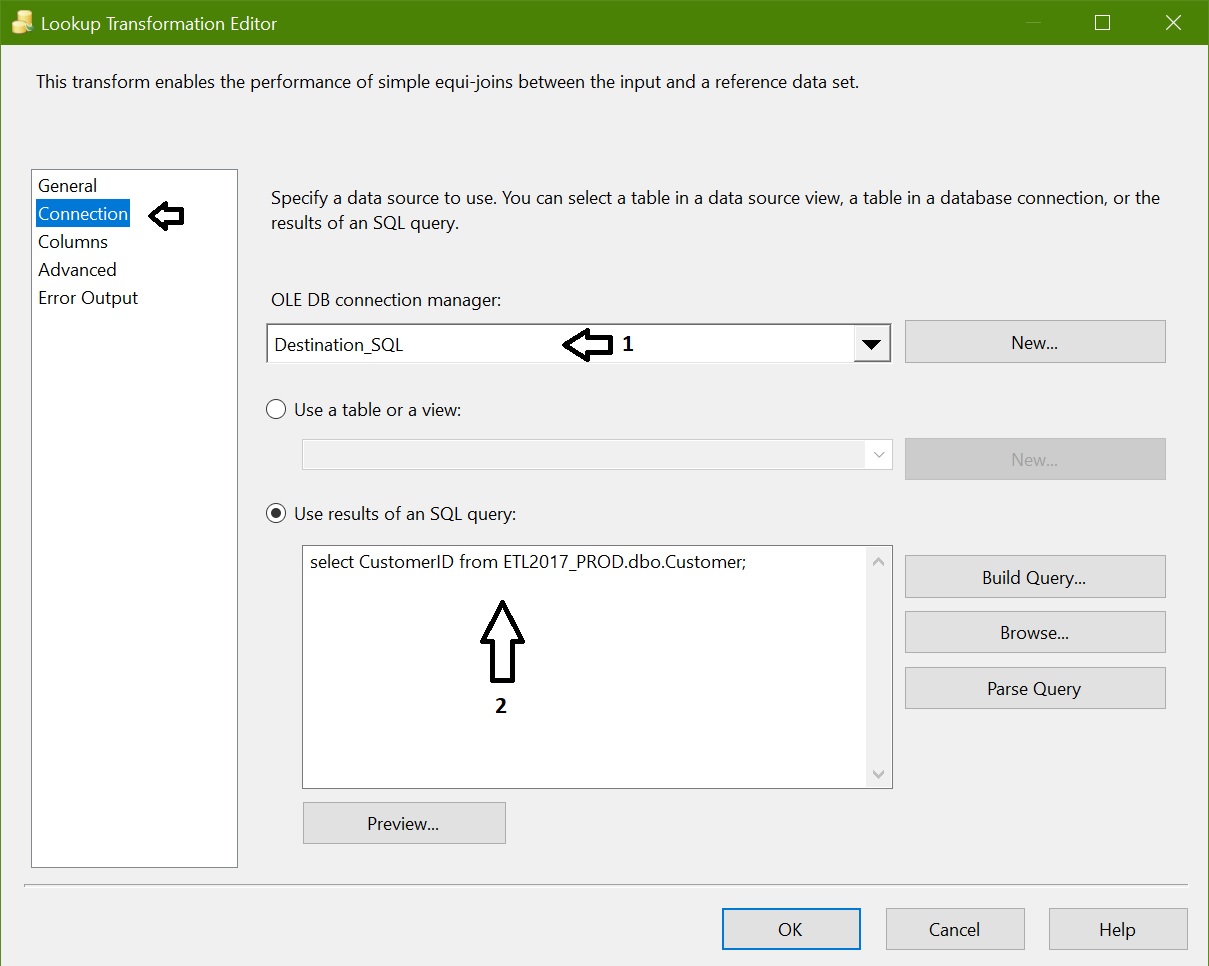
Add lookup transformation and configure as below
Full Cache: Sine we have a small reference data set we can choose Full Cache option. It means it capture the entire reference set into Memory instead of connecting database every time when required.
Redirect: Rows to No Match when no match found at destination.
Connections: Instead of getting entire table we are using a SQL Query as we required only CustomerID.
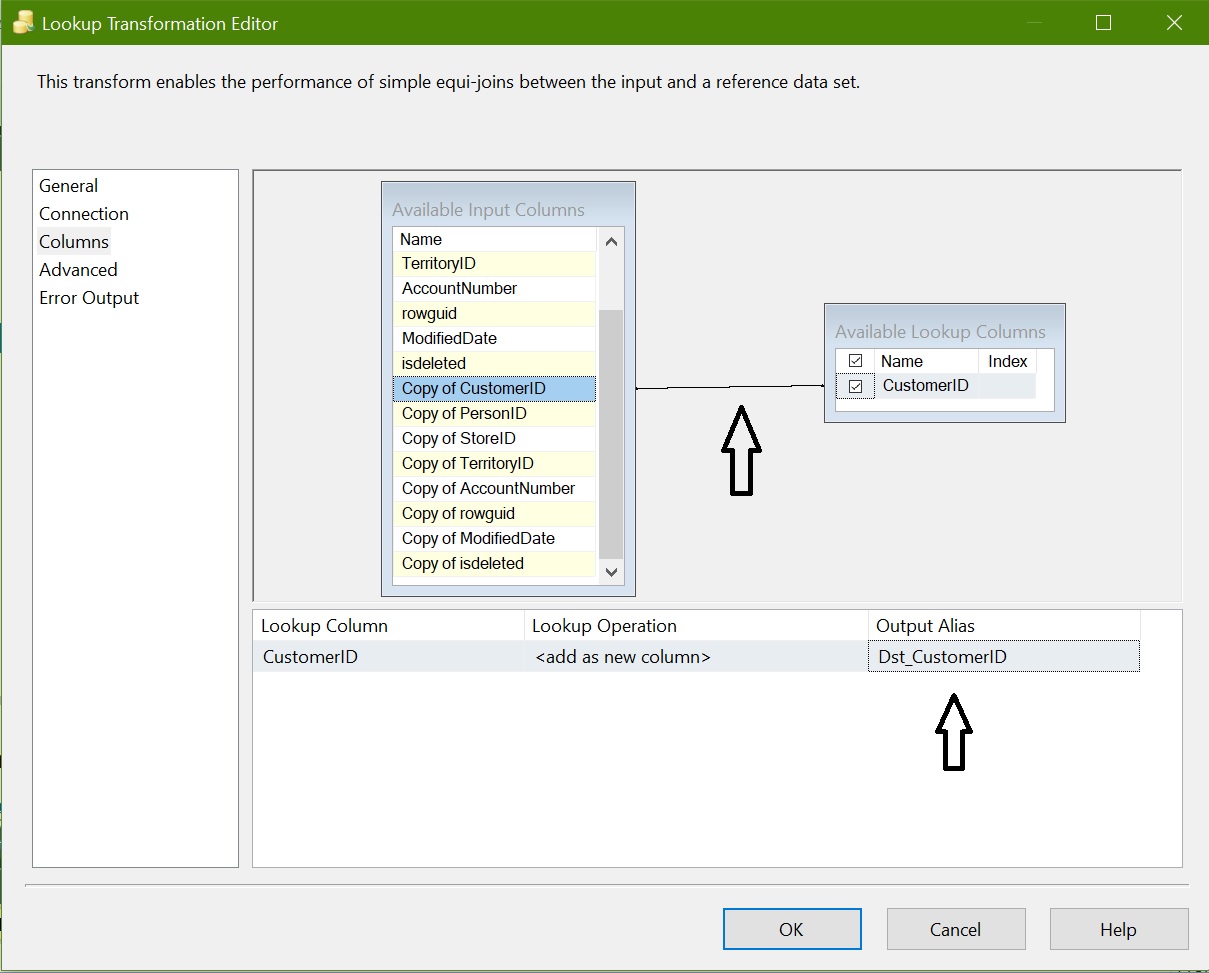
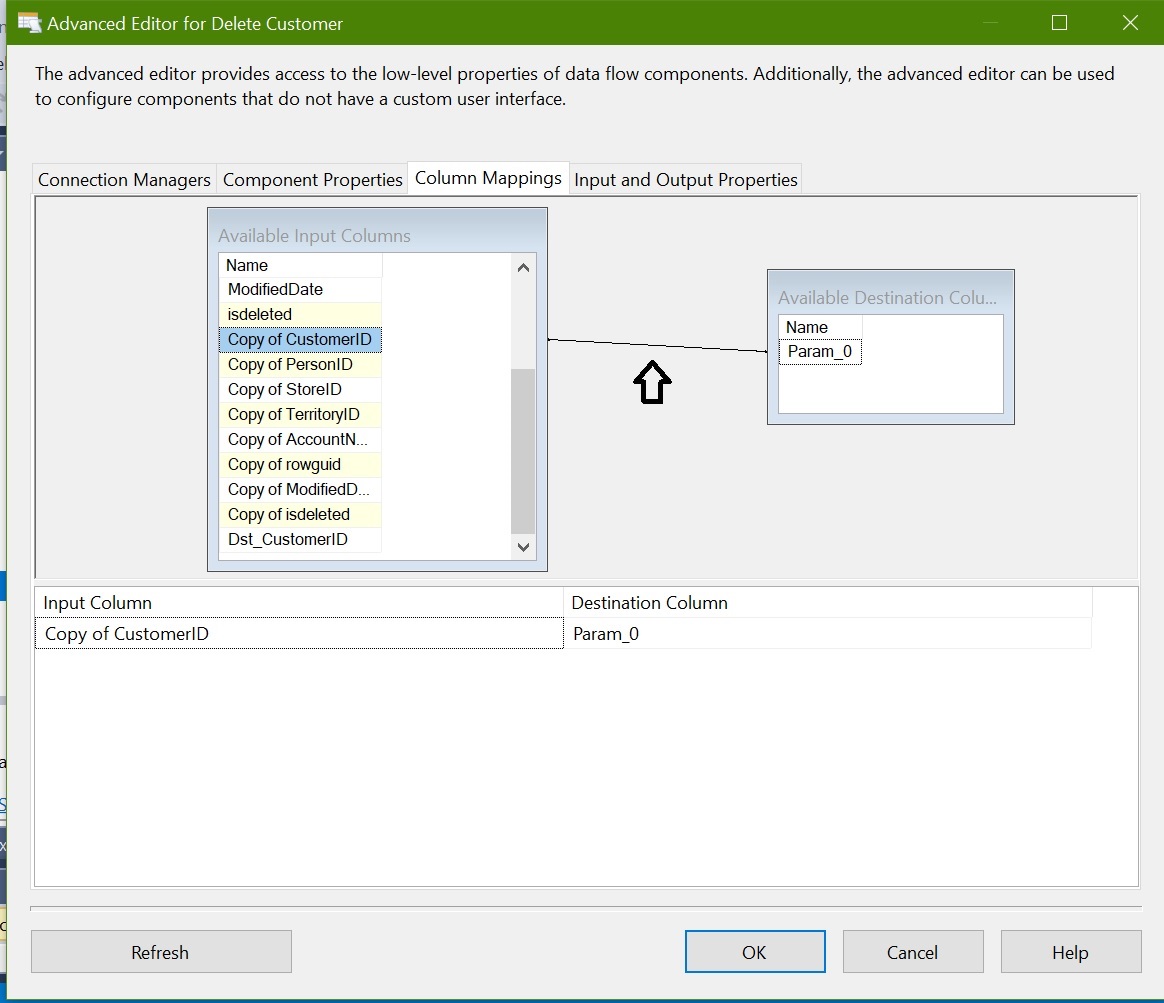
Column Mapping:
Here we are mapping source column “Copy of CustomerID” to destination column “CustomerID”.
To differentiate between source and reference make Output Alias as “Dst_CustomerID”.
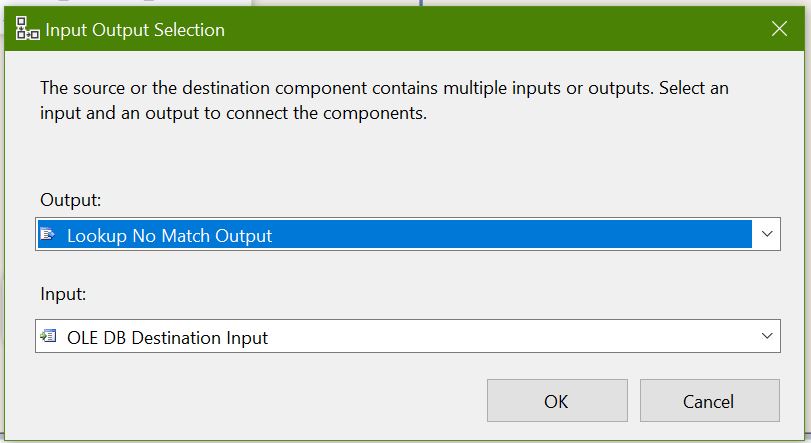
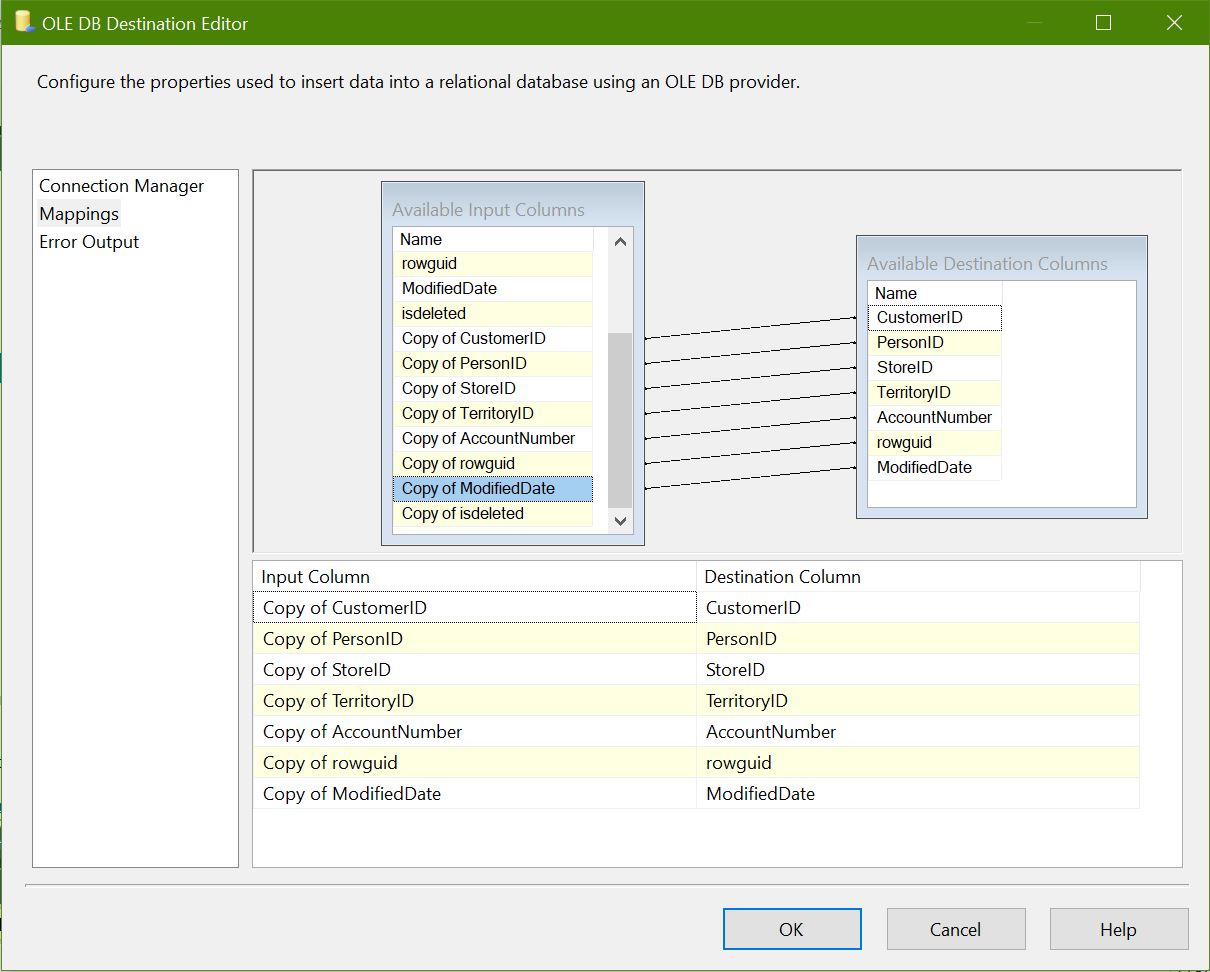
Add a OLEDB Destination and name it as “Insert Customer”. Map No Match output from Lookup to OLEDB Destination:
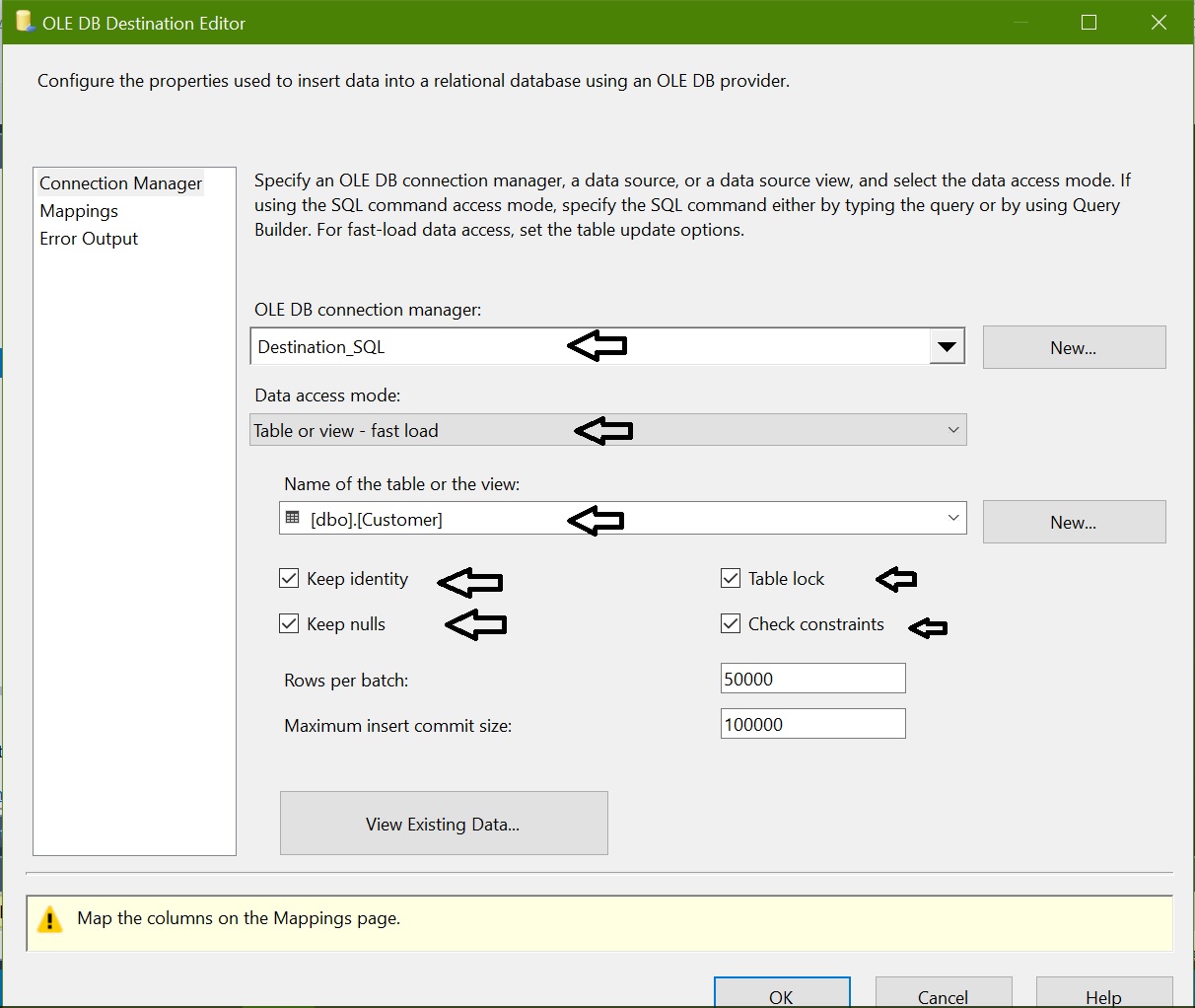
Edit properties for OLEDB Destination “Insert Customer”, connect destination and configure properties and map columns:
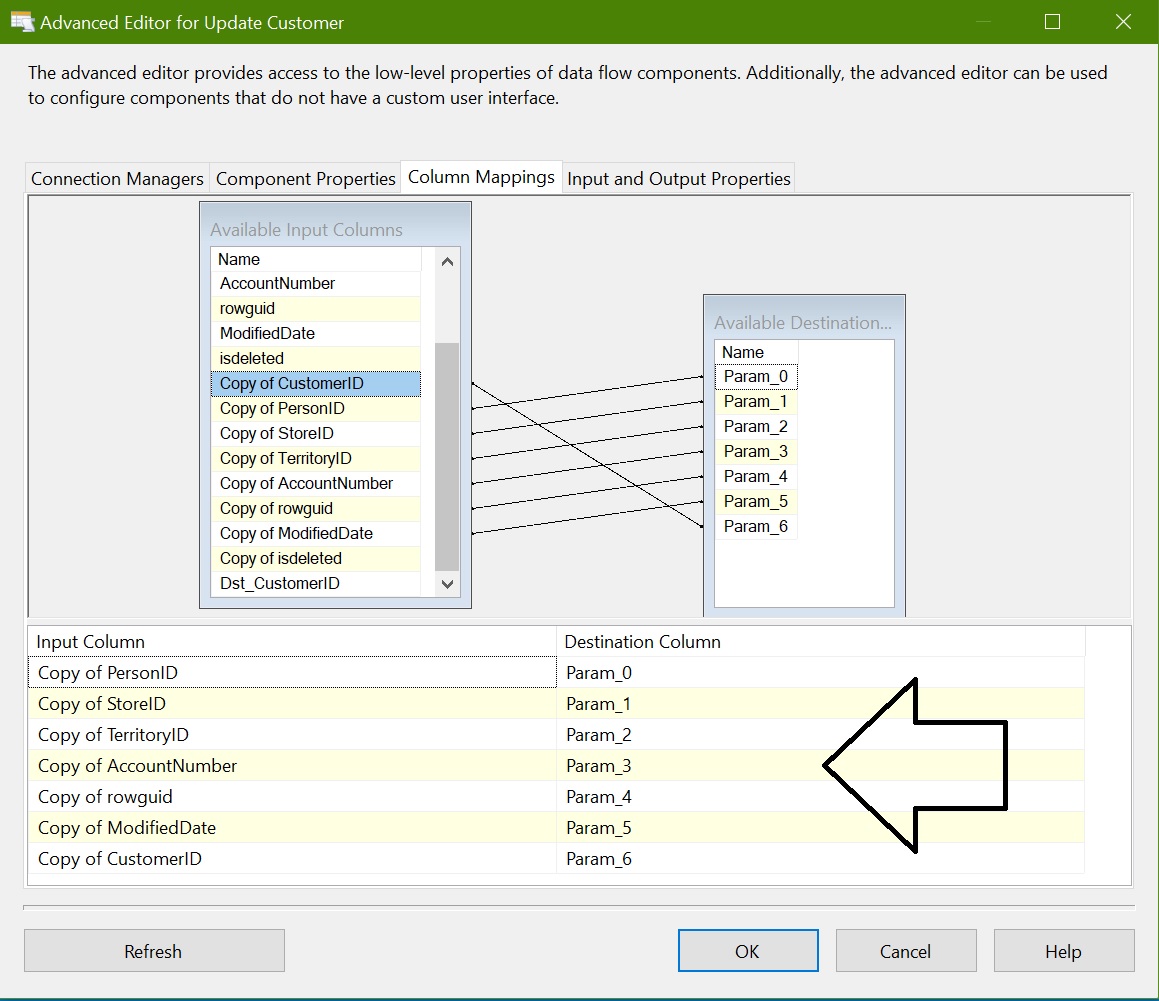
Map columns from converted input columns to destination columns as below:
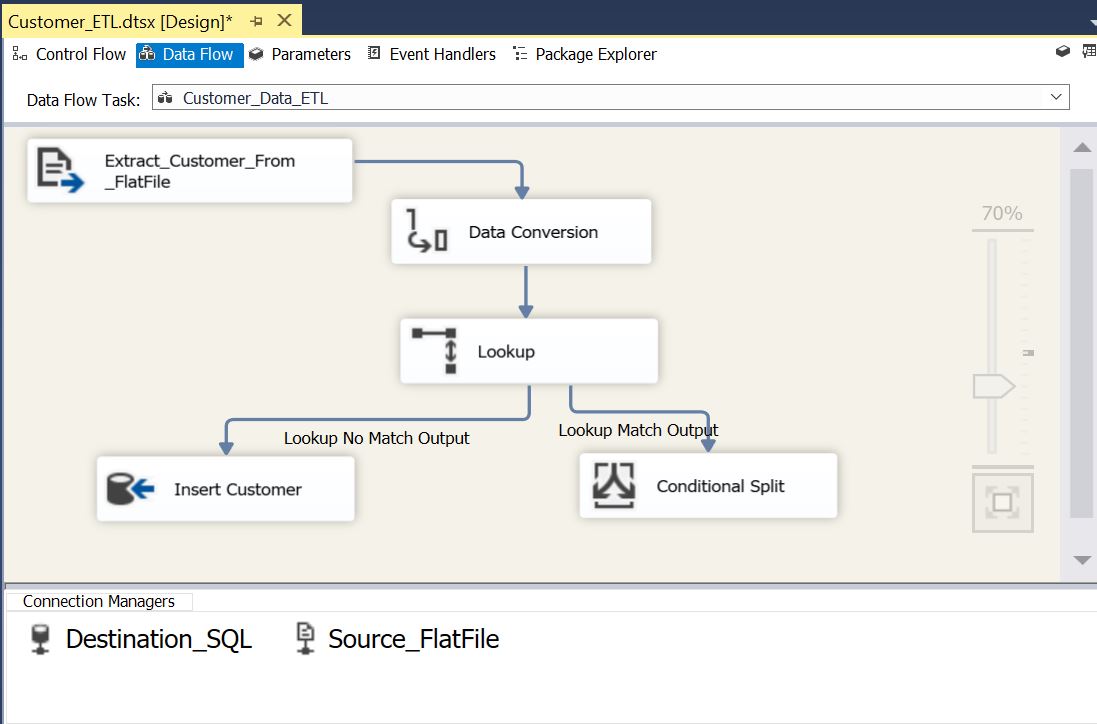
ETL package is ready to handle new customer INSERT. Now we need to handle “Updated” & “Deleted” customers. Add Conditional Split transformation and connect “Lookup Match Output”:
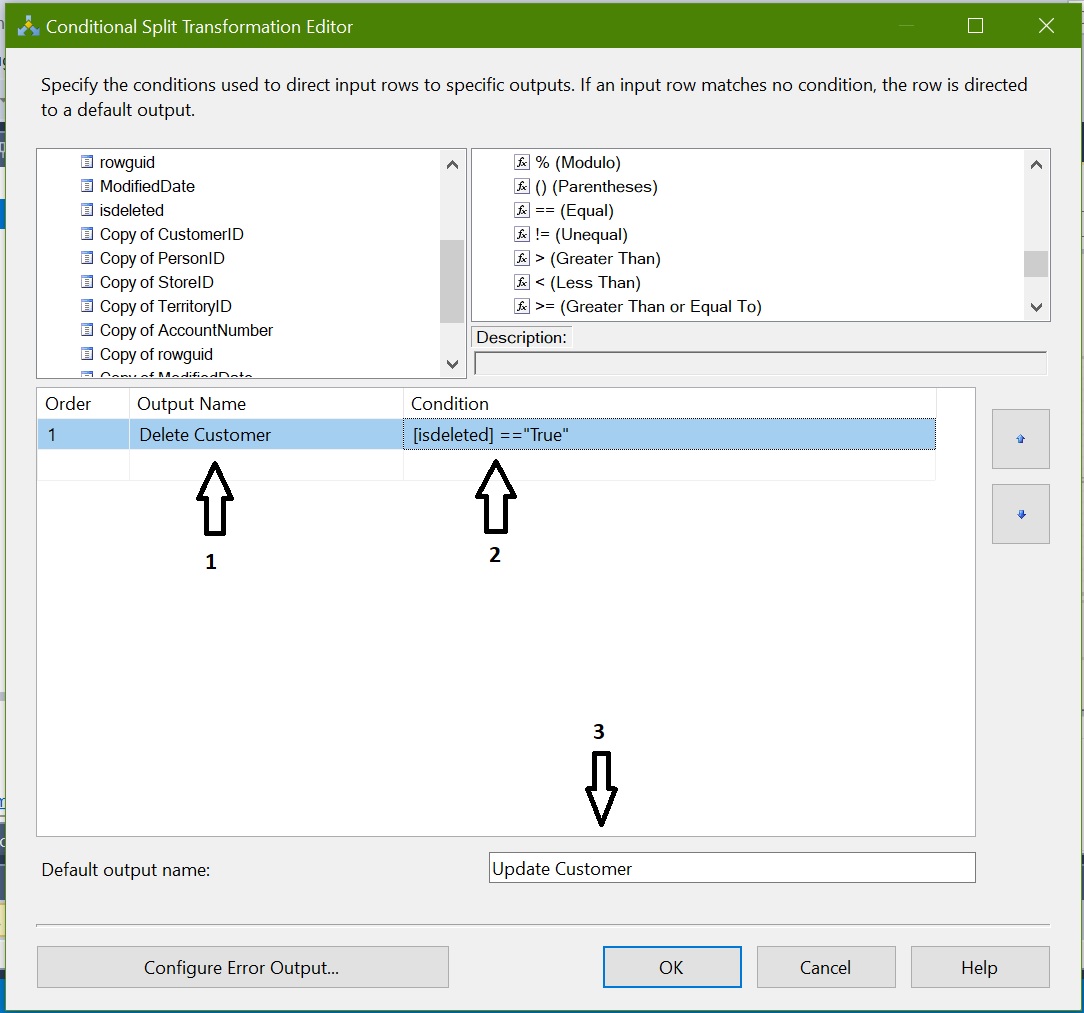
Now we need to configure Conditional Split transformation to identify the Deleted & Updated rows:
Output Name: Name it as “Delete Customer” and apply condition isdeleted == “True”
Default Output Name: “Updated Customer” as remaining all rows comes in default output where isdeleted <> “true”
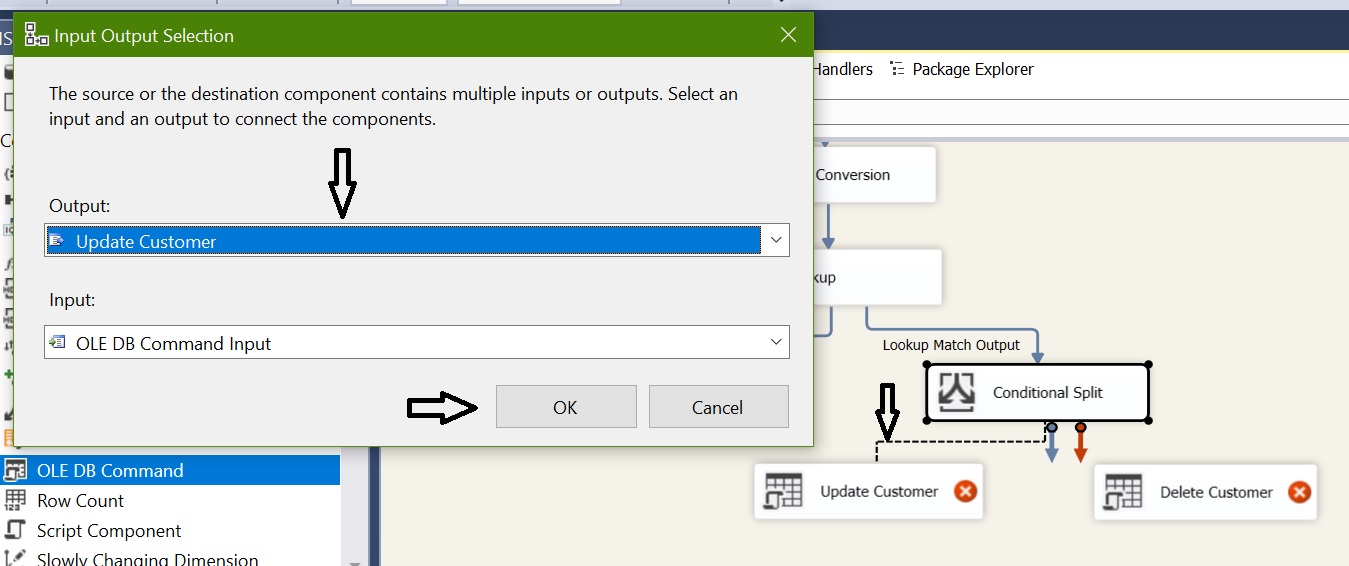
Now we need UPDATE and DELETE customer data in destination for that we are going to use “OLE DB Command”:
Configure OLEDB Command – Update Customer
Configure OLEDB Command – Delete Customer
Finally the package data flow looks like below:
ETL Package Execution:
Case 1: Customer Table is empty and Flat File is having 1702 rows
Case 2: Passing Delta data; 15 New Rows, 10 Updated Rows, 5 Rows with IsDeleted = 1;
Summary:
- This post explains a way to implement incremental data load using SSIS
- We used a small dataset to demonstrate the incremental load
- Most important point to be noted: “OLEDB Command” is a row based operation and execute the SQL Statement for each row coming input row.