–>
SQL SERVER 2005 ARCHITECTURE
Please have a look here to get the full and latest article to know sql server 2005 architecture
SQL Server Architecture
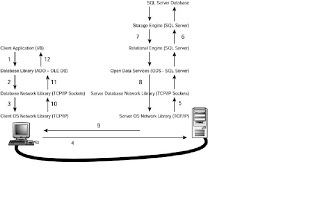
SQL Server is a client/server relational database management system. Figure 1.3 shows the process that every query must follow, from its origin as a SQL query in the client application running in the client computer, to the final result set received by the client application.

Fig: Client access to a SQL Server database
These steps are defined as follows:
1. The user selects an option in a client application. This option calls a function in the client application that generates a query that is sent to SQL Server. The application uses a database access library to send the query in a way SQL Server can understand.
2. The database library transforms the original request into a sequence of one or more Transact-SQL statements to be sent to SQL Server. These statements are encapsulated in one or more Tabular Data Stream (TDS) packets and passed to the database network library to be transferred to the server computer.
3. The database network library uses the network library available in the client computer to repackage the TDS packets as network protocol packets.
4. The network protocol packets are sent to the server computer network library across the network, where they are unwrapped from their network protocol. Chapter 1. Relational Database Management Systems and SQL Server
5. The extracted TDS packets are sent to Open Data Services (ODS), where the original query is extracted.
6. ODS sends the query to the relational engine, where the query is optimized and executed in collaboration with the storage engine.
7. The relational engine creates a result set with the final data and sends it to ODS.
8. ODS builds one or more TDS packets to be sent to the client application, and sends them to the server database network library.
9. The server database network library repackages the TDS packets as network protocol packets and sends them across the network to the client computer.
10. The client computer receives the network protocol packets and forwards them to the network libraries where the TDS packets are extracted.
11. The network library sends the TDS packets to the database access library, where these packets are reassembled and exposed as a client result set to the client application.
12. The client application displays information contained in the result sets to the user.
Services Offered by MSSQL Server 2005:
ØDatebase Engine
ØFulltext Search
ØReplication
ØService Broker
ØIntegration Services
ØReporting Services
ØAnalysis Services
ØNotification Services
Database Engine:
The Database Engine is the core service for storing, processing, and securing data. The Database Engine provides controlled access and rapid transaction processing to meet the requirements of the most demanding data consuming applications within your enterprise.
Analysis Services:
Analysis Services is the core service for supporting rapid analysis of business data, delivering online analytical processing (OLAP) and data mining functionality in business intelligence applications.
Integration Services:
SQL Server 2005 Integration Services (SSIS) is the extract, transform, and load (ETL) component of SQL Server 2005. It replaces the earlier SQL Server ETL component, Data Transformation Services (DTS).
Replication:
Replication is a set of technologies for copying and distributing data and database objects from one database to another, and then synchronizing between databases to maintain consistency. Using replication, you can distribute data to different locations and to remote or mobile users over local and wide area networks, dial-up connections, wireless connections, and the Internet. SQL Server provides three types of replication, each with different capabilities: transactional replication, merge replication, and snapshot replication.
Reporting Services:
SQL Server 2005 Reporting Services (SSRS) is a server-based reporting platform that provides comprehensive data reporting from relational and multidimensional data sources. Reporting Services includes processing components, a complete set of tools that you can use to create and manage reports, and an application programming interface (API) that allows developers to integrate or extend data and report processing in custom applications.
Notification Services:
SQL Server 2005 Notification Services is a platform for developing applications that generate and send notifications, and it is also an engine that runs those applications. You can use Notification Services to generate and send timely, personalized messages to thousands or even millions of subscribers, and deliver the messages to a wide variety of applications and devices.
Full-Text Search:
SQL Server contains the functionality you need to issue full-text queries against plain character-based data in SQL Server tables. Full-text queries could include words and phrases or multiple forms of a word or phrase. Full-Text Search allows fast and flexible indexing for keyword-based query of text data stored in a Microsoft SQL Server database. In SQL Server 2005, Full-Text Search delivers enterprise-level search functionality.
Service Broker:
SQL Server 2005 Service Broker provides the SQL Server Database Engine native support for messaging and queuing applications. This makes it easier for developers to create sophisticated applications that use the Database Engine components to communicate between disparate databases. Developers can use Service Broker to easily build distributed and reliable applications.
Components Installed with SQL Server
When you install SQL Server you install two different sets of components:
· Server components are back-end services, responsible for data storage, data integrity, security, concurrency, and so on.
. Client components are front-end applications, used by administrators, developers, and even end users, to administer, develop, test, and use a SQL Server database system.
Components Installed:
- Microsoft SQL Server service (MSSQLServer)— The main service, responsible for data storage, data integrity, consistency, concurrency, security, query processing, optimization, and execution.
- Microsoft SQL Server Agent (SQLServerAgent)— Responsible for scheduling jobs, managing alerts, and Notifying operators. SQL Server Agent is an important service in SQL Server Administration because so many administrative operations depend on it to be executed automatically at fixed intervals— for example, backups, data consistency checks, rebuilding indexes, importing and exporting data, replication, and so on.
- Microsoft Search— Provides full-text search capabilities to SQL Server, as well as to Microsoft Exchange and Index Server.
- Microsoft SQL Server OLAP Service— Provides back-end support for Analysis Services.
- Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MS-DTC)— Provides transaction support in multiserver and heterogeneous environments.
- Server Network libraries— SQL Server can listen to several network libraries at the same time, waiting for queries to answer, and use any of these libraries to send results to the client. The selected database network library must have a compatible server network library to work with. SQL Server 2000 currently supports the following network libraries: TCP/IP Sockets, Named Pipes, Multiprotocol, NWLink IPX/SPX, VIA ServerNET II SAN, VIA GigaNet SAN, Banyan VINES, and AppleTalk
Services Installed with Sql Server 2005
- Database Services
- Integration Services
- Analysis Services
- Reporting Services
- Notification and Broker Services
- Client Components
ØConnectivity Components
ØManagement Tools
ØConnectivity Components
ØBusiness Intelligence Development Studio
ØSoftware Development Kit
ØSQL XML Client Features
ØLegacy Components
- Documentation, Samples and Sample Databases
Tools and Utilities Available with Sql Server:
Sql Server 2000:
Enterprise Manager
Query Analyzer
Profiler
Upgrade Wizard
Service Manager
Command-line utilities
Sql Server 2005:
SQL Server Management Studio
Sqlcmd Utility
SQL Configuration Manager
Database Engine Tuning Advisor
Query Editor
Surface Area Configuration
SQL Server Profiler
Tablediff Utility
Sql Server 2008:
SQL Management Objects
SQL Configuration Manager
Sqlcmd Utility
SQL Server Management Studio
SQL Profiler
SQL Server Agent
Database Tuning Advisor
Microsoft Operations Manager Pack
Resource Governor
Performance Studio
Editions Of Sql Server:
Three are types of Editions Available:
à Core Editions
ØEnterprise
ØStandard
à Specialized Editions
ØWork Group
ØWeb
ØDeveloper
à Free Editions
ØExpress
ØCompact
Enterprise:
Enterprise workloads that need redundancy and built-in Business Intelligence
Standard:
Shared data scenarios in departments and small to large businesses
Work Group:
Remote offices that need local instances of company data
Web:
For web application hosting
Developer:
Full featured edition for development and testing only
Express:
Entry level database, ideal for learning and ISV redistribution
Compact:
Embedded database for developing desktop and mobile applications















